The USB standard has evolved over time, and with each new version, it has brought improvements in transfer speed and compatibility.
In this guide, we'll try to clarify a bit the confusion with the names of the USB standard, although it has been more than 5 years since the name change in the USB standard, it never hurts to refresh our memory.
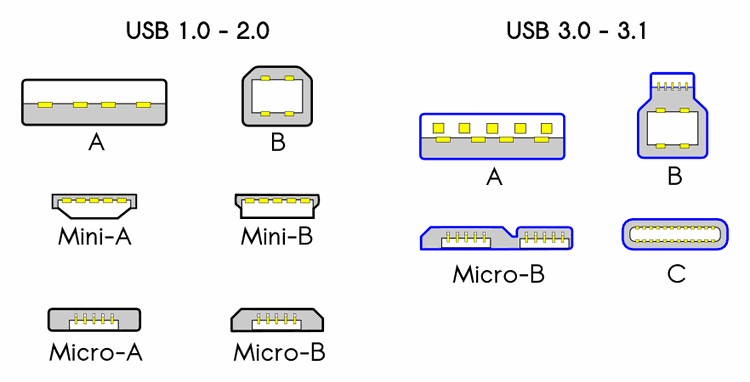
USB 1.0/1.1: Initially launched as USB 1.0, later revised as USB 1.1. These versions were the first to be widely adopted and offered transfer speeds of up to 12 Mbps.
USB 2.0: Also known as High-Speed USB, it offered transfer speeds of up to 480 Mbps, making it significantly faster than previous versions. It was a major upgrade and became the dominant standard for many years.
USB 3.2 Gen 1: It's a revision of the USB 3.1 Gen 1 standard (previously USB 3.0). It maintains the transfer speed of 5 Gbps. Also called "SuperSpeed USB".
USB 3.2 Gen 2: Previously known as USB 3.1. This version increases the transfer speed to 10 Gbps, maintaining the characteristics of previous versions in terms of power management and protocol efficiency. Also called "SuperSpeed USB 10 Gbps".
USB 3.2 Gen 2x2: Previously known as USB 3.2. It introduces a transfer speed of up to 20 Gbps. Also known as "SuperSpeed USB 20Gbps".
USB 4.0: Represents a significant advancement in USB technology, offering faster transfer speeds (up to 40 Gbps) and greater device connectivity versatility. It combines the features of Thunderbolt 3 and USB 3.2, offering faster transfer speeds and greater compatibility.

Although there are different types of connectors, such as microUSB, USB-A, USB-B, USB-C, they are simply connectors. What's important to know for connection speed is to understand the protocol specification; having a USB-C port doesn't always guarantee maximum transfer speed, charging, etc.
USB-C is a type of connector used for cables and devices. It is characterized by being reversible. It is capable of supporting various technologies, including USB 3.1/3.2, DisplayPort, Thunderbolt, and Power Delivery. It doesn't have specific versions, as USB-C refers to the type of physical connector. However, the characteristics and capabilities of devices using USB-C may vary depending on the versions of the USB standard and other compatible technologies.
Power Delivery (PD) is a specification that allows power delivery through a USB cable. It enables faster and more efficient charging of compatible devices. PD can provide different power levels, from a few watts to over 100W, depending on the capabilities of devices and compatible chargers. Different versions of Power Delivery are related to different power profiles that can be delivered. Power profiles include 5V/3A, 9V/3A, 15V/3A, and 20V/5A, among others.
DisplayPort over USB-C allows video signals to be transmitted through a USB-C cable or docking. It allows connecting USB-C compatible devices to external monitors with resolutions of up to 4K and beyond. Versions of DisplayPort over USB-C are closely tied to the versions of DisplayPort and USB-C specifications used. For example, DisplayPort 1.2 and DisplayPort 1.4 are common in devices compatible with DisplayPort over USB-C.

Thunderbolt: Utilizing the USB-C connector, Thunderbolt offers extremely fast data transfer speeds, along with support for video, power charging, and other protocols. Developed by Intel in collaboration with Apple, Thunderbolt is compatible with DisplayPort over USB-C and can support higher video resolutions and refresh rates than standard versions of DisplayPort over USB-C. It also provides daisy-chaining capabilities, allowing several devices to be connected in series through a single Thunderbolt port.
